Kaldi-nnet3-基础知识
Kaldi Nnet3文档的描述
nnet1 和 nnet2 都是的基于Component(组件)对象设计,从而神经网络可以看作是Component的堆叠。每个Component有支持minibatch的Propagate和Backprop函数,以及其他函数。
nnet1和nnet2除了支持按顺序堆叠非线性变换外,通过额外的设计,也支持一些其他功能.
- 在nnet1里,可以用components中嵌套components实现更复杂的网络topo,比如ParallelComponent,该Component中可以包含多组Component序列。另外,LSTM是在C++层定义一个专用的Componet来实现的。
- 在nnet2里,网络设计中加入了时间index的概念,从而支持把不同时间帧的数据(包括中间层的输出)拼起来一起使用,可以支持TDNN这种模型。
Nnet3的目标是在支持Nnet1和Nnet2已支持的topo基础上在支持更多的网络类型,同时提供基于配置文件的方式去构建网络,从而用户不需要做代码开发就可以实现新的网络结构的ideas。在Nnet3中,可以用最基本的组件直接构建LSTM。
Kaldi的Nnet3网络结构。
- xconfig: 类似于keras,简洁的网络定义,xconfig覆盖了大部分常用的神经网络layer
- config: kaldi实际使用的config, 基于node定义网络结构,如果xconfig无法满足需求,可在config层实现。
- C++: 如果某些网络无法用config构建,或者想提高效率,则可以在C++层实现。(Kaldi本身的LSTM可以通过config实现,但是Kaldi也在C++层实现了一个更高效的LSTM)
xconfig定义网络
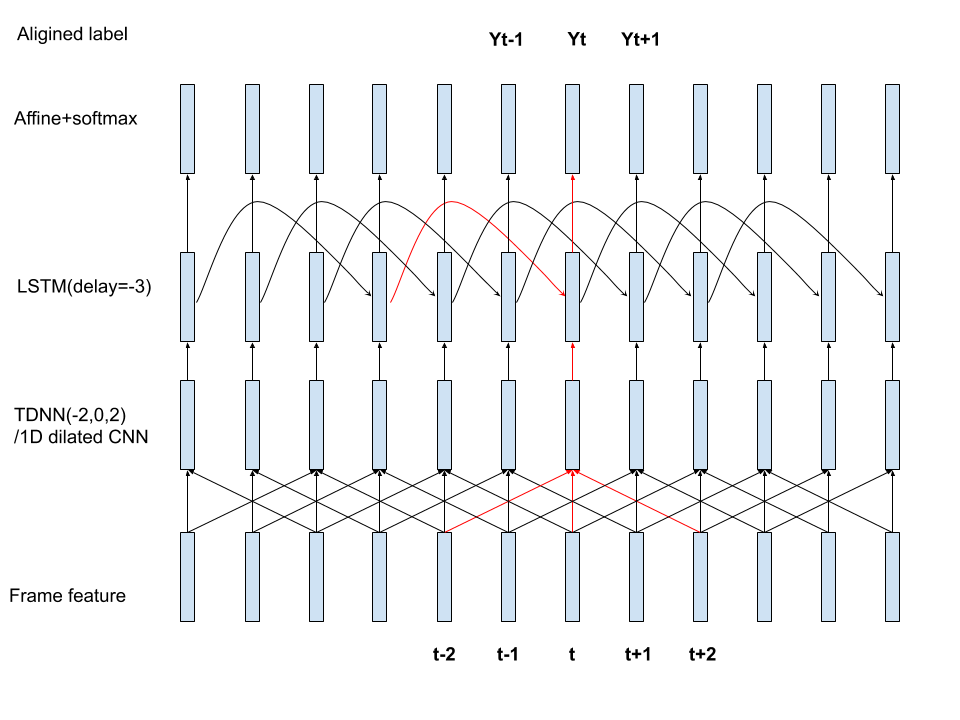
假如要定义如下网络
特征40维,
1层tdnn,输出64维,t时刻的上下文依赖(t-2,t,t+2)
1层lstm,cell/输出 32维, t时刻依赖t-3时刻的recurrent输入(一般t时刻依赖t-1时刻,但是kaldi里经常做3帧的跳帧)
10维softmax输出。
对应的xconfig文件为
#tdnn-lstm.xconfig
input dim=40 name=input
relu-batchnorm-layer name=tdnn dim=64 input=Append(-2,0,2)
fast-lstm-layer name=lstm cell-dim=32 decay-time=20 delay=-3
output-layer name=output input=lstm dim=10 max-change=1.5
其网络的拓扑如下图
config网络定义
使用下面脚本,可以将xconifg转换为Kaldi Nnet3实际使用的config文件。
steps/nnet3/xconfig_to_configs.py --xconfig-file tdnn-lstm.xconfig --config-dir ./
tdnn-lstm.xconfig转换后的网络如下,可以看到基于config的定义比较长。
input-node name=input dim=40
component name=tdnn.affine type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=120 output-dim=64 max-change=0.75
component-node name=tdnn.affine component=tdnn.affine input=Append(Offset(input, -2), input, Offset(input, 2))
component name=tdnn.relu type=RectifiedLinearComponent dim=64 self-repair-scale=1e-05
component-node name=tdnn.relu component=tdnn.relu input=tdnn.affine
component name=tdnn.batchnorm type=BatchNormComponent dim=64 target-rms=1.0
component-node name=tdnn.batchnorm component=tdnn.batchnorm input=tdnn.relu
### Begin LTSM layer 'lstm'
# Gate control: contains W_i, W_f, W_c and W_o matrices as blocks.
component name=lstm.W_all type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=96 output-dim=128 max-change=1.5
# The core LSTM nonlinearity, implemented as a single component.
# Input = (i_part, f_part, c_part, o_part, c_{t-1}), output = (c_t, m_t)
# See cu-math.h:ComputeLstmNonlinearity() for details.
component name=lstm.lstm_nonlin type=LstmNonlinearityComponent cell-dim=32 max-change=0.75
# Component for backprop truncation, to avoid gradient blowup in long training examples.
component name=lstm.cm_trunc type=BackpropTruncationComponent dim=64 clipping-threshold=30.0 zeroing-threshold=15.0 zeroing-interval=20 recurrence-interval=3 scale=1.0
### Nodes for the components above.
component-node name=lstm.W_all component=lstm.W_all input=Append(tdnn.batchnorm, IfDefined(Offset(lstm.m_trunc, -3)))
component-node name=lstm.lstm_nonlin component=lstm.lstm_nonlin input=Append(lstm.W_all, IfDefined(Offset(lstm.c_trunc, -3)))
dim-range-node name=lstm.m input-node=lstm.lstm_nonlin dim-offset=32 dim=32
component-node name=lstm.cm_trunc component=lstm.cm_trunc input=lstm.lstm_nonlin
dim-range-node name=lstm.c_trunc input-node=lstm.cm_trunc dim-offset=0 dim=32
dim-range-node name=lstm.m_trunc input-node=lstm.cm_trunc dim-offset=32 dim=32
### End LTSM layer 'lstm'
component name=output.affine type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=32 output-dim=10 max-change=1.5 param-stddev=0.0 bias-stddev=0.0
component-node name=output.affine component=output.affine input=lstm.m
component name=output.log-softmax type=LogSoftmaxComponent dim=10
component-node name=output.log-softmax component=output.log-softmax input=output.affine
output-node name=output input=output.log-softmax objective=linear
其中的依赖关系如下图。
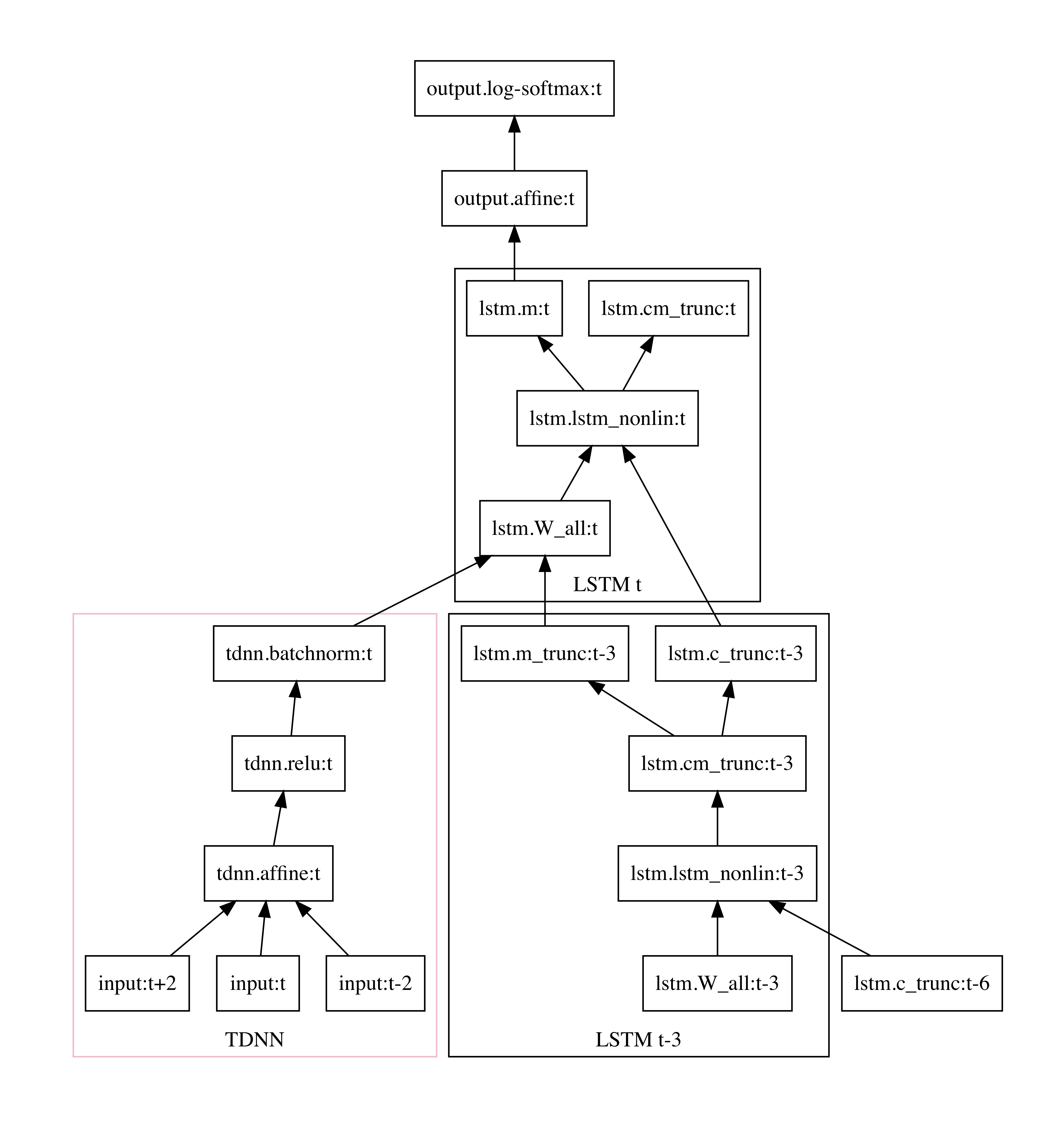
nnet3网络定义
nnet3网络是由node组成的有向无环拓扑图。node有batch和时间维度的概念,语法中支持如下的node
- component-node Kaldi提供的基础组件
- dim-range-node 从上一层输出的矩阵中选取特定范围维度。
- descriptor-node 起到胶水作用,提供一些方法将node组合连接起来
- output-node/input-node
component-node
component-node是对component的实例化。一般先定义一个component,再定义该component的component-node
定义component时需要设置的属性
- name 该component的名字
- type 该component的Component类型
- type的属性 不同的Component类型支持的属性
component-node时需要设置的属性
- name 该component-node的名字,可以被其他node的input属性引用
- component 该component-node的component类型
- input 该component-node的输入node
如下先定义了输入120维,输出64维的NaturalGradientAffineComponent类型的component,叫做tdnn.affine。
input-node name=input dim=40
component name=tdnn.affine type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=120 output-dim=64 max-change=0.75
component-node name=tdnn.affine component=tdnn.affine input=Append(Offset(input, -2), input, Offset(input, 2))
再定义一个name为tdnn.affine的component-node(这里component-node和component的名字一样都叫tdnn.affine,但是这不是必要的), 其input属性中引用了name为input的input-node。 注意区分input属性和name为input的节点。
也可以按如下定义,和上面是等价的。
input-node name=mfcc_input dim=40
component name=tdnn.affine type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=120 output-dim=64 max-change=0.75
component-node name=tdnn.affine.node component=tdnn.affine input=Append(Offset(mfcc_input, -2), mfcc_input, Offset(mfcc_input, 2))
descriptor-node
descriptor-node提供一些常用操作,连接其他node。 descriptor-node的语法和其他node不同,其并不单独定义一行,一般出现在input中,上面配置里Append/IfDefined/Offset均为descriptor-node。
比如下例中,Append(Offset(input, -2), input, Offset(input, 2)),表示将input节点在t-2,t,t+2位置的值作为拼接起来,作为tdnn.affine的输入.
component name=tdnn.affine type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=120 output-dim=64 max-change=0.75
component-node name=tdnn.affine component=tdnn.affine input=Append(Offset(input, -2), input, Offset(input, 2))
可见Kaldi nnet3 config层并不提供TDNN的component,而是在对Affine层的输入利用Append+Offset实现了1维Dilated卷积,也就是TDNN. 但是kaldi在xconfig层面提供TDNN。
下面例子例子,中的IfDefined也是一个descriptor-node,表示如果改值存在则使用,否则使用一个零值量。
component name=lstm.W_all type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=96 output-dim=128 max-change=1.5
component-node name=lstm.W_all component=lstm.W_all input=Append(tdnn.batchnorm, IfDefined(Offset(lstm.m_trunc, -3)))
dim-range-node
lstm.lstm_nonlin节点(关于该节点,可参考下一节C++的LSTM实现中的介绍)的输出,是单个矩阵(batch_size * dim),其中包含了cell和output,分别占据0-31维和32-63维,所以用两个dim-range-node分别取出。 其中的lstm.cm_trunc是为了做Recurrent方向上的BPTT用的,因为太长的梯度会有可能梯度爆炸。
component-node name=lstm.lstm_nonlin component=lstm.lstm_nonlin input=Append(lstm.W_all, IfDefined(Offset(lstm.c_trunc, -3)))
dim-range-node name=lstm.m input-node=lstm.lstm_nonlin dim-offset=32 dim=32
component-node name=lstm.cm_trunc component=lstm.cm_trunc input=lstm.lstm_nonlin
dim-range-node name=lstm.c_trunc input-node=lstm.cm_trunc dim-offset=0 dim=32
dim-range-node name=lstm.m_trunc input-node=lstm.cm_trunc dim-offset=32 dim=32
C++
在Kaldi中,实现LSTM,可以基于最基本的组件,比如用sigmond/tanh/affine编写config实现。
xconfig中的lstm-layer即使用该方法,但是生成的config非常繁琐,而且也不高效。xconfig提供了一个fast-lstm-layer,其中在C++层面实现了LstmNonlinearityComponent,该Component封装了LSTM的 计算,从而config的定义更简洁。
这里以LstmNonlinearityComponent为例看一下C++层。其他的层也可按类似方法分析。
Kaldi的注释非常详细,LstmNonlinearityComponent的注释如下:
/*
LstmNonlinearityComponent is a component that implements part of an LSTM, by
combining together the sigmoids and tanh's, plus some diagonal terms, into
a single block.
We will refer to the LSTM formulation used in
Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network Architectures for Large Scale Acoustic Modeling"
by H. Sak et al,
http://static.googleusercontent.com/media/research.google.com/en//pubs/archive/43905.pdf.
Suppose the cell dimension is C. Then outside this component, we compute
the 4 * C-dimensional quantity consisting of 4 blocks as follows, by a single
matrix multiplication:
i_part = W_{ix} x_t + W_{im} m_{t-1} + b_i
f_part = W_{fx} x_t + W_{fm} m_{t-1} + b_f
c_part = W_{cx} x_t + W_{cm} m_{t-1} + b_c
o_part = W_{ox} x_t + W_{om} m_{t-1} + b_o
The part of the computation that takes place in this component is as follows.
Its input is of dimension 5C [however, search for 'dropout' below],
consisting of 5 blocks: (i_part, f_part, c_part, o_part, and c_{t-1}). Its
output is of dimension 2C, consisting of 2 blocks: c_t and m_t.
To recap: the input is (i_part, f_part, c_part, o_part, c_{t-1}); the output is (c_t, m_t).
This component has parameters, 3C of them in total: the diagonal matrices w_i, w_f
and w_o.
In the forward pass (Propagate), this component computes the following:
i_t = Sigmoid(i_part + w_{ic}*c_{t-1}) (1)
f_t = Sigmoid(f_part + w_{fc}*c_{t-1}) (2)
c_t = f_t*c_{t-1} + i_t * Tanh(c_part) (3)
o_t = Sigmoid(o_part + w_{oc}*c_t) (4)
m_t = o_t * Tanh(c_t) (5)
# note: the outputs are just c_t and m_t.
[Note regarding dropout: optionally the input-dimension may be 5C + 3 instead
of 5C in this case, the last three input dimensions will be interpreted as
per-frame dropout masks on i_t, f_t and o_t respectively, so that on the RHS of
(3), i_t is replaced by i_t * i_t_scale, and likewise for f_t and o_t.]
The backprop is as you would think, but for the "self-repair" we need to pass
in additional vectors (of the same dim as the parameters of the layer) that
dictate whether or not we add an additional term to the backpropagated
derivatives. (This term helps force the input to the nonlinearities into the
range where the derivatives are not too small).
This component stores stats of the same form as are normally stored by the
StoreStats() functions for the sigmoid and tanh units, i.e. averages of the
activations and derivatives, but this is done inside the Backprop() functions.
[the StoreStats() functions don't take the input data as an argument, so
storing this data that way is impossible, and anyway it's more efficient to
do it as part of backprop.]
Configuration values accepted:
cell-dim e.g. cell-dim=1024 Cell dimension. The input
dimension of this component is cell-dim * 5, and the
output dimension is cell-dim * 2. Note: this
component implements only part of the LSTM layer,
see comments above.
param-stddev Standard deviation for random initialization of
the diagonal matrices (AKA peephole connections).
default=1.0, which is probably too high but
we couldn't see any reliable gain from decreasing it.
tanh-self-repair-threshold Equivalent to the self-repair-lower-threshold
in a TanhComponent; applies to both the tanh nonlinearities.
default=0.2, you probably won't want to change this.
sigmoid-self-repair-threshold Equivalent to self-repair-lower-threshold
in a SigmoidComponent; applies to all three of the sigmoid
nonlinearities. default=0.05, you probably won't want to
change this.
self-repair-scale Equivalent to the self-repair-scale in a SigmoidComponent
or TanhComponent; applies to both the sigmoid and tanh
nonlinearities. default=1.0e-05, which you probably won't
want to change unless dealing with an objective function
that has smaller or larger dynamic range than normal, in
which case you might want to make it smaller or larger.
*/
从注释中可以看到,该Component
- 输入为 (i_part, f_part, c_part, o_part, c_{t-1})
- 输出为 (c_t, m_t)
其中i_part, f_part, c_part, o_part的计算Gate和新Cell中跟x和m相关(即LSTM外部输入)的部分。
i_part = W_{ix} x_t + W_{im} m_{t-1} + b_i
f_part = W_{fx} x_t + W_{fm} m_{t-1} + b_f
c_part = W_{cx} x_t + W_{cm} m_{t-1} + b_c
o_part = W_{ox} x_t + W_{om} m_{t-1} + b_o
i_part, f_part, c_part, o_part的计算由lstm.W_all层的输出提供。注意这里使用t-3的recurrent连接,所以是m_{t-3}.
component name=lstm.W_all type=NaturalGradientAffineComponent input-dim=96 output-dim=128 max-change=1.5
component-node name=lstm.W_all component=lstm.W_all input=Append(tdnn.batchnorm, IfDefined(Offset(lstm.m_trunc, -3)))
用一个全联接层就可以完成上面四组计算
\[\left( \begin{array}{c} i_{part} \\ f_{part} \\ c_{part} \\ o_{part} \end{array} \right) = \left( \begin{array}{cc} W_{ix} & W_{im} \\ W_{fx} & W_{fm} \\ W_{cx} & W_{cm} \\ W_{ox} & W_{om} \end{array} \right) \left( \begin{array}{c} x_t \\ m_{t-3} \end{array} \right) + \left( \begin{array}{c} b_i \\ b_f \\ b_c \\ b_o \end{array} \right)\]lstm_nonlin的输入为input=Append(lstm.W_all, IfDefined(Offset(lstm.c_trunc, -3)), 即将lstm.W_all的t时刻输出和lstm.c_trunc的t-3时刻(IfDefined表示若改值不存在,则使用0)输出拼起来。
lstm.c_trunc是从lstm.lstm_nonlin提取出c部分。
注意这里使用t-3的recurrent连接,所以需要的是c_{t-3}.
component name=lstm.lstm_nonlin type=LstmNonlinearityComponent cell-dim=32 max-change=0.75
component-node name=lstm.lstm_nonlin component=lstm.lstm_nonlin input=Append(lstm.W_all, IfDefined(Offset(lstm.c_trunc, -3)))
该网络前向计算完成下面计算:
i_t = Sigmoid(i_part + w_{ic}*c_{t-1}) (1)
f_t = Sigmoid(f_part + w_{fc}*c_{t-1}) (2)
c_t = f_t*c_{t-1} + i_t * Tanh(c_part) (3)
o_t = Sigmoid(o_part + w_{oc}*c_t) (4)
m_t = o_t * Tanh(c_t) (5)
LstmNonlinearityComponent类的Propagate和Backprop对应其前向计算和反向求导的计算。
其中前向计算在 cu::ComputeLstmNonlinearity,分为CPU和GPU实现,其中CPU实现代码如下
CpuComputeLstmNonlinearity(const MatrixBase<Real> &input_mat,
const MatrixBase<Real> ¶ms_mat,
MatrixBase<Real> *output) {
int32 num_rows = input_mat.NumRows(),
input_cols = input_mat.NumCols(),
cell_dim = input_cols / 5;
KALDI_ASSERT(input_cols == (cell_dim * 5) || input_cols == (cell_dim * 5) + 3);
KALDI_ASSERT(output->NumRows() == num_rows);
KALDI_ASSERT(params_mat.NumRows() == 3);
KALDI_ASSERT(params_mat.NumCols() == cell_dim);
KALDI_ASSERT(output->NumCols() == 2 * cell_dim);
MatrixBase<Real> &output_mat = *output;
const Real *params_data = params_mat.Data();
int32 params_stride = params_mat.Stride();
for (int32 r = 0; r < num_rows; r++) {
const Real *input_row = input_mat.RowData(r);
// i_scale and f_scale relate to dropout, they will normally be 1.0.
Real i_scale = (input_cols == cell_dim*5 ? 1.0:input_row[cell_dim*5]),
f_scale = (input_cols == cell_dim*5 ? 1.0:input_row[cell_dim*5 + 1]),
o_scale = (input_cols == cell_dim*5 ? 1.0:input_row[cell_dim*5 + 2]);
Real *output_row = output_mat.RowData(r);
for (int32 c = 0; c < cell_dim; c++) {
Real i_part = input_row[c];
Real f_part = input_row[c + cell_dim];
Real c_part = input_row[c + 2 * cell_dim];
Real o_part = input_row[c + 3 * cell_dim];
Real c_prev = input_row[c + 4 * cell_dim];
Real w_ic = params_data[c];
Real w_fc = params_data[c + params_stride];
Real w_oc = params_data[c + params_stride * 2];
Real i_t = ScalarSigmoid(i_part + w_ic * c_prev);
Real f_t = ScalarSigmoid(f_part + w_fc * c_prev);
Real c_t = f_t * f_scale * c_prev + i_t * i_scale * ScalarTanh(c_part);
Real o_t = ScalarSigmoid(o_part + w_oc * c_t);
Real m_t = o_t * o_scale * ScalarTanh(c_t);
output_row[c] = c_t;
output_row[c + cell_dim] = m_t;
}
}
}
后向的CPU版本在CpuBackpropLstmNonlinearity中,过程更繁琐些。
xconfig支持的组件类型
xconfig支持的layer
#steps/libs/nnet3/xconfig/parser.py
# We have to modify this dictionary when adding new layers
config_to_layer = {
'input' : xlayers.XconfigInputLayer,
'output' : xlayers.XconfigTrivialOutputLayer,
'output-layer' : xlayers.XconfigOutputLayer,
'relu-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'relu-renorm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'relu-batchnorm-dropout-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'relu-dropout-layer': xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'relu-batchnorm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'relu-batchnorm-so-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'batchnorm-so-relu-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'batchnorm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'sigmoid-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'tanh-layer' : xlayers.XconfigBasicLayer,
'fixed-affine-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFixedAffineLayer,
'idct-layer' : xlayers.XconfigIdctLayer,
'affine-layer' : xlayers.XconfigAffineLayer,
'lstm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigLstmLayer,
'lstmp-layer' : xlayers.XconfigLstmpLayer,
'lstmp-batchnorm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigLstmpLayer,
'fast-lstm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastLstmLayer,
'fast-lstm-batchnorm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastLstmLayer,
'fast-lstmp-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastLstmpLayer,
'fast-lstmp-batchnorm-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastLstmpLayer,
'lstmb-layer' : xlayers.XconfigLstmbLayer,
'stats-layer': xlayers.XconfigStatsLayer,
'relu-conv-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-relu-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-renorm-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'relu-conv-renorm-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'batchnorm-conv-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-relu-renorm-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'batchnorm-conv-relu-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'relu-batchnorm-conv-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'relu-batchnorm-noconv-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'relu-noconv-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-relu-batchnorm-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-relu-batchnorm-so-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-relu-batchnorm-dropout-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'conv-relu-dropout-layer': xlayers.XconfigConvLayer,
'res-block': xlayers.XconfigResBlock,
'res2-block': xlayers.XconfigRes2Block,
'channel-average-layer': xlayers.ChannelAverageLayer,
'attention-renorm-layer': xlayers.XconfigAttentionLayer,
'attention-relu-renorm-layer': xlayers.XconfigAttentionLayer,
'attention-relu-batchnorm-layer': xlayers.XconfigAttentionLayer,
'relu-renorm-attention-layer': xlayers.XconfigAttentionLayer,
'gru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigGruLayer,
'pgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigPgruLayer,
'opgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigOpgruLayer,
'norm-pgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigNormPgruLayer,
'norm-opgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigNormOpgruLayer,
'fast-gru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastGruLayer,
'fast-pgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastPgruLayer,
'fast-norm-pgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastNormPgruLayer,
'fast-opgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastOpgruLayer,
'fast-norm-opgru-layer' : xlayers.XconfigFastNormOpgruLayer,
'tdnnf-layer': xlayers.XconfigTdnnfLayer,
'prefinal-layer': xlayers.XconfigPrefinalLayer,
'spec-augment-layer': xlayers.XconfigSpecAugmentLayer,
'renorm-component': xlayers.XconfigRenormComponent,
'batchnorm-component': xlayers.XconfigBatchnormComponent,
'no-op-component': xlayers.XconfigNoOpComponent,
'linear-component': xlayers.XconfigLinearComponent,
'affine-component': xlayers.XconfigAffineComponent,
'scale-component': xlayers.XconfigPerElementScaleComponent,
'dim-range-component': xlayers.XconfigDimRangeComponent,
'offset-component': xlayers.XconfigPerElementOffsetComponent,
'combine-feature-maps-layer': xlayers.XconfigCombineFeatureMapsLayer,
'delta-layer': xlayers.XconfigDeltaLayer
}
config支持的component-node
其对应的C++ Componet如下,可以查看相应NN C++类的实现,可作为学习用,或自己添加新的Componet时参考。
src/nnet3/nnet-simple-component.cc
class PnormComponent
class DropoutComponent
class ElementwiseProductComponent
class SigmoidComponent
class TanhComponent
class RectifiedLinearComponent
class AffineComponent
class BlockAffineComponent
class RepeatedAffineComponent
class NaturalGradientRepeatedAffineComponent
class SoftmaxComponent
class LogSoftmaxComponent
class NaturalGradientAffineComponent
class LinearComponent
class FixedAffineComponent
class SumGroupComponent
class FixedScaleComponent
class FixedBiasComponent
class NoOpComponent
class SumBlockComponent
class ClipGradientComponent
class PermuteComponent
class PerElementScaleComponent
class PerElementOffsetComponent
class ConstantFunctionComponent
class NaturalGradientPerElementScaleComponent
class ScaleAndOffsetComponent
class CompositeComponent
src/nnet3/nnet-convolutional-component.h
class TimeHeightConvolutionComponent
class TdnnComponent
src/nnet3/nnet-combined-component.cc
class ConvolutionComponent
class LstmNonlinearityComponent
class MaxpoolingComponent
class GruNonlinearityComponent
class OutputGruNonlinearityComponent
src/nnet3/nnet-attention-component.cc
class RestrictedAttentionComponent
src/nnet3/nnet-general-component.cc
class DistributeComponent
class StatisticsExtractionComponent
class StatisticsPoolingComponent
class BackpropTruncationComponent
class ConstantComponent
class DropoutMaskComponent
class GeneralDropoutComponent
class SpecAugmentTimeMaskComponent
src/nnet3/nnet-normalize-component.cc
class NormalizeComponent
class BatchNormComponent